Leading Health Indicators 2030: Advancing Health, Equity, and Well-Being
05 de març 2020
28 de febrer 2020
Hyper-personalized medicine is just starting
From technology Review:
Here is our annual list of technological advances that we believe will make a real difference in solving important problems. How do we pick? We avoid the one-off tricks, the overhyped new gadgets. Instead we look for those breakthroughs that will truly change how we live and work.What hyper-personalized medicine stands for?
- Unhackable internet
- Hyper-personalized medicine
- Digital money
- Anti-aging drugs
- AI-discovered molecules
- Satellite mega-constellations
- Quantum supremacy
- Tiny AI
- Differential privacy
- Climate change attribution
Here’s a definition of a hopeless case: a child with a fatal disease so exceedingly rare that not only is there no treatment, there’s not even anyone in a lab coat studying it. “Too rare to care,” goes the saying.
That’s about to change, thanks to new classes of drugs that can be tailored to a person’s genes. If an extremely rare disease is caused by a specific DNA mistake—as several thousand are—there’s now at least a fighting chance for a genetic fix.
One such case is that of Mila Makovec, a little girl suffering from a devastating illness caused by a unique genetic mutation, who got a drug manufactured just for her. Her case made the New England Journal of Medicine in October, after doctors moved from a readout of her genetic error to a treatment in just a year. They called the drug milasen, after her.
The treatment hasn’t cured Mila. But it seems to have stabilized her condition: it has reduced her seizures, and she has begun to stand and walk with assistance.
Mila’s treatment was possible because creating a gene medicine has never been faster or had a better chance of working. The new medicines might take the form of gene replacement, gene editing, or antisense (the type Mila received), a sort of molecular eraser, which erases or fixes erroneous genetic messages. What the treatments have in common is that they can be programmed, in digital fashion and with digital speed, to correct or compensate for inherited diseases, letter for DNA letter.
How many stories like Mila’s are there? So far, just a handful.
But more are on the way. Where researchers would have once seen obstacles and said “I’m sorry,” they now see solutions in DNA and think maybe they can help.
The real challenge for “n-of-1” treatments (a reference to the number of people who get the drug) is that they defy just about every accepted notion of how pharmaceuticals should be developed, tested, and sold. Who will pay for these drugs when they help one person, but still take large teams to design and manufacture?
—Antonio Regalado
27 de febrer 2020
Allocating drugs by lottery
Novartis has held the first draw to choose four babies who will receive its one-shot treatment for the genetic disease spinal muscular atrophy, Zolgensma (onasemnogene abeparvovec), amid criticism of its lottery programme from patient groups and EU health ministers.Does this makes any sense? In my opinion is a perfect strategy (for Novartis) to create artificial scarcity. It is a well known approach to increase willingness to access/ willingness to pay. It was described by Adam Brandenburger in a book long time ago: Coopetition.
Priced in the United States at $2.1m (£1.6m; €1.9m), the most expensive drug course of treatment ever, Zolgensma is not yet approved elsewhere. In December the company announced a plan to give away 50 treatments in other countries over the next six months, the recipients to be chosen randomly from among applicants every two weeks.
Recipients must be under 2, the upper age limit for which the drug is approved in the US. Most of the children in the Zolgensma draw were registered by their doctors. About one child in every 8000 live births is born with spinal muscular atrophy. The most severe type, called type 1 or Werdnig-Hoffmann disease, usually causes death during early childhood if untreated.
I hope it will not succeed (at least in Europe).
David Hockney
21 de febrer 2020
Predictive modeling in health care (2)
Data-Driven Approaches for Health Care Machine Learning for Identifying High Utilizers
Predicting health outcomes using data modeling approaches is an emerging field that can reveal important insights into disproportionate spending patterns. This book presents data driven methods, especially machine learning, for understanding and approaching the high utilizers problem, using the example of a large public insurance program.Five years ago I explained in this blog our experience on predictive modeling. This a key reference book.
20 de febrer 2020
Confidential drug pricing without confidential prices
Performance-based managed entry agreements for new medicines in OECD countries and EU member states: How they work and possible improvements going forward
In this blog I've explained my position against confidential prices for drugs. However, there is an option to complicate it: confidential entry agreements. This is the current trend for high cost drugs with uncertain outcome. The report of the OECD explains the current situation in different countries and helps to shed light in this important issue. Just take this short statement and you'll be convinced of the complete mess:
In this blog I've explained my position against confidential prices for drugs. However, there is an option to complicate it: confidential entry agreements. This is the current trend for high cost drugs with uncertain outcome. The report of the OECD explains the current situation in different countries and helps to shed light in this important issue. Just take this short statement and you'll be convinced of the complete mess:
It is difficult to assess to what extent performance-based MEAs have so far been successful. Few countries have formally evaluated their experience. Confidentiality of agreements continues to be a barrier to independent evaluation and little evidence is public. However, information available from expert interviews and from prior studies indicates that CED agreements have so far had a poor track record of reducing uncertainty around the performance of medicines. As a result, some countries have recently reformed CED schemes and some are discontinuing CED agreements altogether in favour of alternatives. The latter include restricted or conditional coverage without a MEA, whereby coverage is initially restricted to certain indications or patient groups and only broadened if and when additional evidence becomes available. Payment-by-result agreements continue to be used quite widely, but they do not always generate evidence
on product performance because data used for triggering payments are not always aggregated and analysed.
15 de febrer 2020
Trade-offs in algorithmic clinical decision making
On the ethics of algorithmic decision-making in healthcare
Great article.
Great article.
Clinicians, or their respective healthcare institutions, are facing a dilemma: while there is plenty of evidence of machine learning algorithms outsmarting their human counterparts, their deployment comes at the costs of high degrees of uncertainty. On epistemic grounds, relevant uncertainty promotes risk-averse decision-making among clinicians, which then might lead to impoverished medical diagnosis. From an ethical perspective, deferring to machine learning algorithms blurs the attribution of accountability and imposes health risks to patients. Furthermore, the deployment of machine learning might also foster a shift of norms within healthcare. It needs to be pointed out, however, that none of the issues we discussed presents a knockout argument against deploying machine learning in medicine.
14 de febrer 2020
Repairing DNA: a review
The promise and challenge of therapeutic genome editing
Jenifer Doudna publishes a must read review article on genome editing in Nature this week.
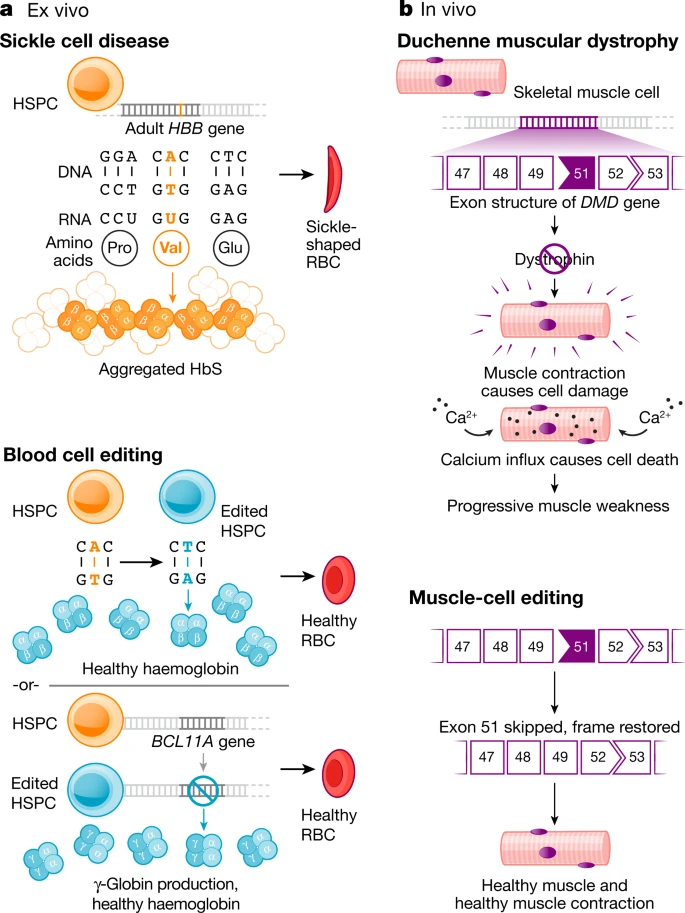
Fig. 1: Ex vivo and in vivo genome editing to treat human disease.
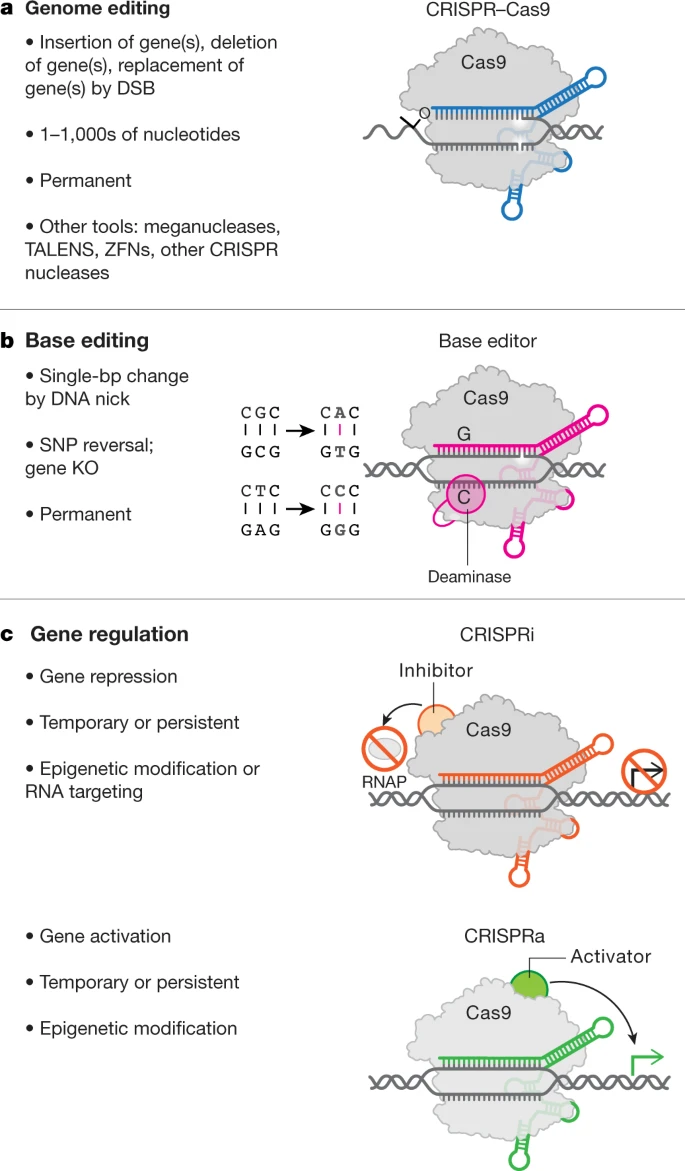
Fig. 2: The genome editing toolbox.
Jenifer Doudna publishes a must read review article on genome editing in Nature this week.
Current clinical trials using the CRISPR platform aim to improve chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell effectiveness, treat sickle cell disease and other inherited blood disorders, and stop or reverse eye disease. In addition, clinical trials to use genome editing for degenerative diseases including for patients with muscular dystrophy are on the horizon.
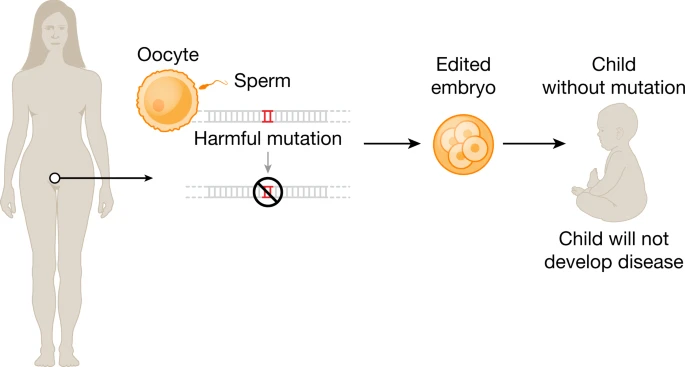
Notably, all of the genome-editing therapeutics under development aim to treat patients through somatic cell modification. These treatments are designed to affect only the individual who receives the treatment, reflecting the traditional approach to disease mitigation. However, genome editing offers the potential to correct disease causing mutations in the germline, which would introduce genetic changes that would be passed on to future generations.
At the time of writing, international commissions convened by the World Health Organization (WHO) and by the US National Academy of Sciences and National Academy of Medicine, together with the Royal Society, are drafting detailed requirements for any potential future clinical use.Meanwhile, CRISPR is closer than you think.
Fig. 1: Ex vivo and in vivo genome editing to treat human disease.
Fig. 2: The genome editing toolbox.
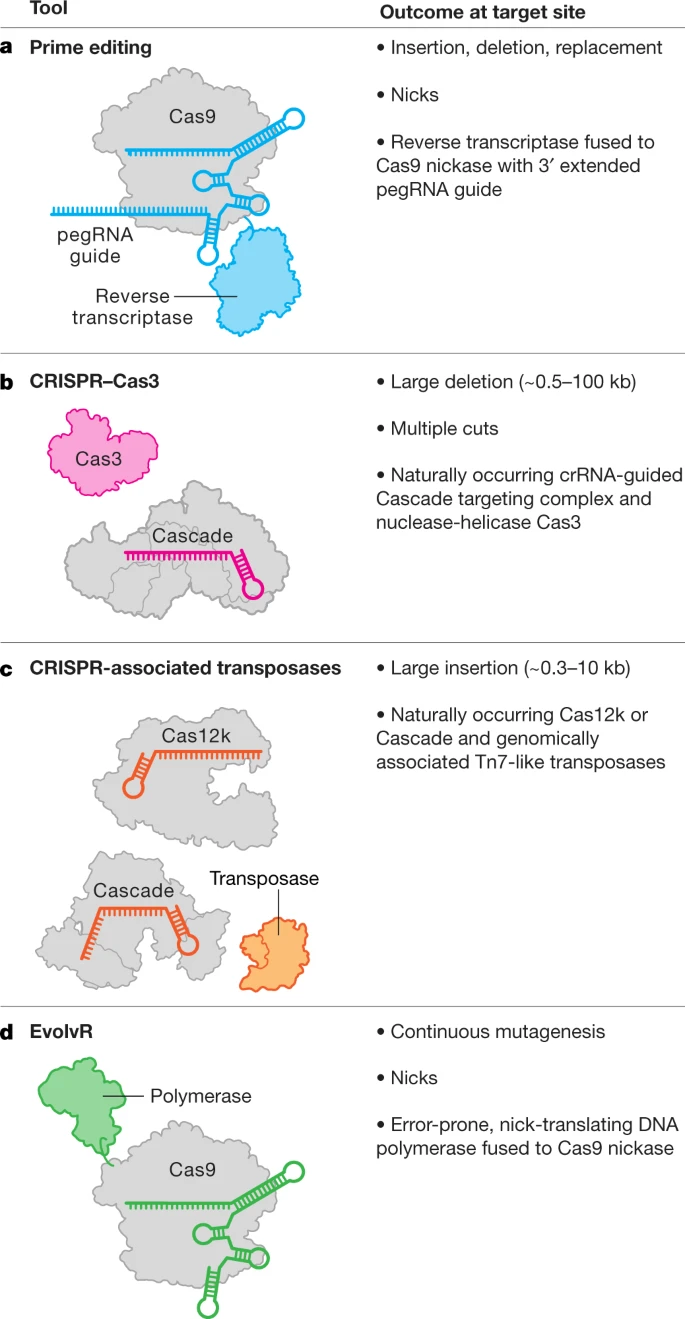
Fig. 3: Emerging tools.
Fig. 4: Editing the human germline.
13 de febrer 2020
Germline genome editing under scrutiny
Societal and Ethical Impacts of Germline Genome Editing: How Can We Secure Human Rights?
Geneva Statement on Heritable Human Genome Editing: The Need for Course Correction
A CRISPR Moratorium Isn't Enough: We Need a Boycott
The Human Right to Science and the Regulation of Human Germline Engineering
The last frontier in genome editing (if it exists) is germline. The special issue of The Crispr journal on bioethics contains an article of special interest and proposes a third process for evaluating individual and societal harms: a Human Rights Impact Assessment.
PS. CRISPR in 2020 Two major reports on germline editing, from the National Academies/Royal Society and the World Health Organization, will be released in 2020. We hope the reports will coordinate, with all the voices of CRISPR being heard, so we can build consensual and broadly acceptable frameworks to ensure we use CRISPR responsibly, especially regarding usage in human embryos for germline editing. The public has asked for it, and the community has been working on it. The science versus society gap will be bridged.
Geneva Statement on Heritable Human Genome Editing: The Need for Course Correction
A CRISPR Moratorium Isn't Enough: We Need a Boycott
The Human Right to Science and the Regulation of Human Germline Engineering
The last frontier in genome editing (if it exists) is germline. The special issue of The Crispr journal on bioethics contains an article of special interest and proposes a third process for evaluating individual and societal harms: a Human Rights Impact Assessment.
Human germline alteration is possible, due in part to democratization of genetic tools required for genome editing, and international scientific and legislative bodies are developing frameworks to manage the ramifications of this technology. Common among these frameworks are two pillars: public engagement and foundational principles. These components are necessary for respecting the autonomy of individuals and for fair processes and respecting diverse values.
However, they are not sufficient for protecting the most vulnerable members of society who may not even be in a position to participate in democratic processes. We propose implementing a HRIA, which captures concerns of public health and offers an opportunity to evaluate and anticipate the societal impact of GGE iteratively as the technology advances, public sentiments evolve, and cultural contexts shift. We recognize that this will raise new challenges of how such assessments are shared and implemented and how they can be enforced. We urge regulatory bodies and policy makers to consider this assessment approach in helping to establish robust regulatory frameworks necessary for the global protection of human rights.And the Geneva Statement on Heritable Human Genome Editing says:
No decision about whether to pursue heritable human genome modification can be legitimate without broadly inclusive and substantively meaningful public engagement and empowerment. Such deliberations may be challenging and messy. They will take time and organizing them will necessitate creativity, hard work, and significant human and financial resources. The course correction proposed here is essential to these efforts.I agree.
We must in the meantime respect the predominant policy position against pursuing heritable human genome modification, if we are to prevent individual scientists or small committees from making this momentous decision for us all. This will preserve time to cultivate an informed and engaged public that can consider and discuss the societal consequences of altering the genes of future generations and make wise, democratic decisions about the shared future we aspire to build.
PS. CRISPR in 2020 Two major reports on germline editing, from the National Academies/Royal Society and the World Health Organization, will be released in 2020. We hope the reports will coordinate, with all the voices of CRISPR being heard, so we can build consensual and broadly acceptable frameworks to ensure we use CRISPR responsibly, especially regarding usage in human embryos for germline editing. The public has asked for it, and the community has been working on it. The science versus society gap will be bridged.
06 de febrer 2020
Digital health next to you
Bringing health care to the patient: An overview of the use of telemedicine in OECD countries
Benchmarking deployment of eHealth among general practitioners
EHEALTH TREND BAROMETER: ANNUAL EUROPEAN EHEALTH SURVEY 2019
Several reports have been recently released. I would like to highlight the first one by the OECD, it reviews the current state of telemedicine and explains what works. In my opinion we do need an assessment of cost effectiveness of telemedicine, otherwise technology driven change is not enough.
Benchmarking deployment of eHealth among general practitioners
EHEALTH TREND BAROMETER: ANNUAL EUROPEAN EHEALTH SURVEY 2019
Several reports have been recently released. I would like to highlight the first one by the OECD, it reviews the current state of telemedicine and explains what works. In my opinion we do need an assessment of cost effectiveness of telemedicine, otherwise technology driven change is not enough.
Telemedicine services have the potential to improve effectiveness, efficiency and equity in health care, helping policy makers respond to increasing patient demands and needs. However, telemedicine interventions can also introduce new risks and amplify existing inequalities. In order for countries to maximise the benefits and limit the risks, telemedicine services need to improve the quality of care and provide clear benefits for patients. Telemedicine programmes that do not have benefits for patients are not worth pursuing and detract attention from other more effective interventions.
Josep Segú - Central Park
31 de gener 2020
Health services research as a data science
Health Services Evaluation
Health Services Information: Key Concepts and Considerations in Building Episodes of Care from
Administrative Data
Assessing health systems
Health Services Information: Key Concepts and Considerations in Building Episodes of Care from
Administrative Data
Assessing health systems
The provision of relevant, accurate, and timely performance information can play a pivotal role in ensuring the health system is able to deliver effective and efficient health services. Through its capacity to secure accountability in the health system, to determine appropriate treatment paths for patients, and to plan for future service patterns and structures, information can be used to identify and implement potential improvements in service delivery
30 de gener 2020
AI in clinical decision making
International evaluation of an AI system for breast cancer screening
Artificial intelligence is capable of surpassing human experts in breast cancer prediction. You can check it in Nature:
Powered by Google.
Artificial intelligence is capable of surpassing human experts in breast cancer prediction. You can check it in Nature:
To assess its performance in the clinical setting, we curated a large representative dataset from the UK and a large enriched dataset from the USA. We show an absolute reduction of 5.7% and 1.2% (USA and UK) in false positives and 9.4% and 2.7% in false negatives. We provide evidence of the ability of the system to generalize from the UK to the USA. In an independent study of six radiologists, the AI system outperformed all of the human readers: the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC-ROC) for the AI system was greater than the AUC-ROC for the average radiologist by an absolute margin of 11.5%.If AI outperforms radiologists, than there is no argument to delay its implementation.
Powered by Google.
23 de gener 2020
How to distort priority setting?
Biases distorting priority setting
Why priority setting in health care has so poor outcomes while relevant systems are well developed and readily available? You just have to read this article to understand it.
Why priority setting in health care has so poor outcomes while relevant systems are well developed and readily available? You just have to read this article to understand it.
It starts to identify some rational and structural explanations for the discrepancy between theoretical efforts and practical outcomes in priority setting. However, even if these issues are addressed, practical priority setting may still not obtain its goals. This is because a wide range of irrational effects is hampering priority setting: biases.
Table 1. Overview of various biases and potential implications for priority setting and at which level they may be most prominent.
| Bias | Potential Implications | Level |
|---|---|---|
| Identifiability and Singularity effect | Undermining principles | Micro |
| Rejection Dislike | Hamper disinvestment | Micro, meso |
| Failure Embarrassment effect | Overuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Prominence Effect (Opportunity Cost Neglect) | Non-warranted use | All |
| Status Quo Bias | Overuse, Underuse | All |
| Endowment Effect | Overuse, Underuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Loss Aversion | Hamper disinvestment | All |
| Aversion to Risk / Ambiguity | Overuse | Micro, meso |
| Availability Heuristics | Overuse | Micro, meso |
| Sacred Values and Taboo trade-offs | Undermining principles | All |
| Progress bias | Overuse | All |
| Adoption Addiction | Overuse | Micro, macro |
| Complexity bias | Undermining principles, overuse | Micro, meso, macro |
| Extension bias | Overuse | All |
| Asymmetry of risks and benefits | Overuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Positive cognitive feedback loops | Undermining principles, overuse | Micro, meso, macro |
| Prestige bias | Undermining principles, overuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Imperative of Action | Undermining principles, overuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Technology Placebo Effect | Undermining principles, overuse | Micro (primarily) |
| Imperative of Knowledge | Overuse | Micro |
| Competency Effect | Overuse | Micro |
| Multiple Replacements | Overuse | Micro |
| White Elephants | Overinvestment | Micro |
| Boys and Toys Effect | Unwarranted use | Micro |
17 de gener 2020
Episode based payment systems (2)
Value-based provider payment: towards a theoretically preferred design
The details of a payment system methodology are clearly described in this article. I was not surprised to confirm that the proposals we made two decades ago were in the same direction: two-part payment, fix and variable. Unfortunately nowadays we have a retrofuture system that nobody knows exactly how incentives really work. Of course, this is the first best for a discretionary behaviour by a resource allocator. This is a clear step in the wrong direction that started a decade ago. Without proper incentives, efficiency suffers, and to be clear this means less efficient healthcare for the patients. Unfortunately again, nobody cares about it.
The details of a payment system methodology are clearly described in this article. I was not surprised to confirm that the proposals we made two decades ago were in the same direction: two-part payment, fix and variable. Unfortunately nowadays we have a retrofuture system that nobody knows exactly how incentives really work. Of course, this is the first best for a discretionary behaviour by a resource allocator. This is a clear step in the wrong direction that started a decade ago. Without proper incentives, efficiency suffers, and to be clear this means less efficient healthcare for the patients. Unfortunately again, nobody cares about it.
The main contribution of this paper is twofold. Inspired by the societal debate on whatThe time to fix the current mess has arrived.
stakeholders in health care should ideally strive for, as well as by existing definitions of value, we first described and further specified the concept of value, facilitating the specification of requirements in the design of VBP. We conclude that, in this respect, value is ideally conceptualised as a multifaceted concept, comprising not only high quality of care at the lowest possible costs but also efficient cooperation, innovation and health promotion. Second, starting from these value dimensions, we derived various design features of a theoretically preferred VBP model. We conclude that in order to stimulate value in a broad sense, the payment should consist of two main components that must be carefully designed. The first component is a risk-adjusted global base payment with risk-sharing elements paid to a multidisciplinary provider group for the provision of (virtually) the full continuum of care to a certain population. The second
component is a relatively low-powered variable payment that explicitly rewards aspects of value that can be adequately measured.
Jordi Sàbat
16 de gener 2020
Episode based payment systems
Unraveling the Complexity in the Design and Implementation of Bundled Payments: A Scoping Review of Key Elements From a Payer’s Perspective
After per case based payment systems (DRGs) everybody was waiting for a comprehensive system to measure health services activities. And instead of focusing on episodes, what happened is that bundling was the new frame. Unfortunately, after all these years bundling has not provided the answer because the scope of measurement is related to several diseases and it is not holistic.
When everybody was asking for an alternative to fee-for service, the answer was in my opinion "patient focused episodes of care", but the US government decided otherwise and protected the interests of those that leverage fee-for-service.
Therefore, now it is the time to fix this mistake and take the right road. In this article you'll find some issues to consider when you have to design a payment system. It still talks about bundling, forget it, substitute it by episodes and it will be fine.
After per case based payment systems (DRGs) everybody was waiting for a comprehensive system to measure health services activities. And instead of focusing on episodes, what happened is that bundling was the new frame. Unfortunately, after all these years bundling has not provided the answer because the scope of measurement is related to several diseases and it is not holistic.
When everybody was asking for an alternative to fee-for service, the answer was in my opinion "patient focused episodes of care", but the US government decided otherwise and protected the interests of those that leverage fee-for-service.
Therefore, now it is the time to fix this mistake and take the right road. In this article you'll find some issues to consider when you have to design a payment system. It still talks about bundling, forget it, substitute it by episodes and it will be fine.
Our framework provides a structured overview of the principal, literature‐based elements of the design and implementation of bundled payment contracts from a payer's perspective. We identified 53 elements that involve all procurement phases and relate to actors on all levels of the health care system. A better understanding of these elements can help payers and other actors devise a strategic approach and reduce the complexity of implementing these contracts. Compared with traditional FFS models, bundled payment contracts introduce an alternative set of financial incentives that affect the entire health care system, involve almost all aspects of governance within organizations, and demand a different type of collaboration among organizations. This is what makes the design and implementation of bundled payment contracts complex and is why they should not be strategically approached by payers as merely the adoption of a new contracting model but, rather, as part of a broader transformation to a more sustainable value‐based health care system, based less on short‐term transactional negotiations and more on long‐term collaborative relationships between payers and providers.
Subscriure's a:
Missatges (Atom)