COVID-19 diagnostics in context
This is the best summary of current supply of diagnostic tests for Covid-19:
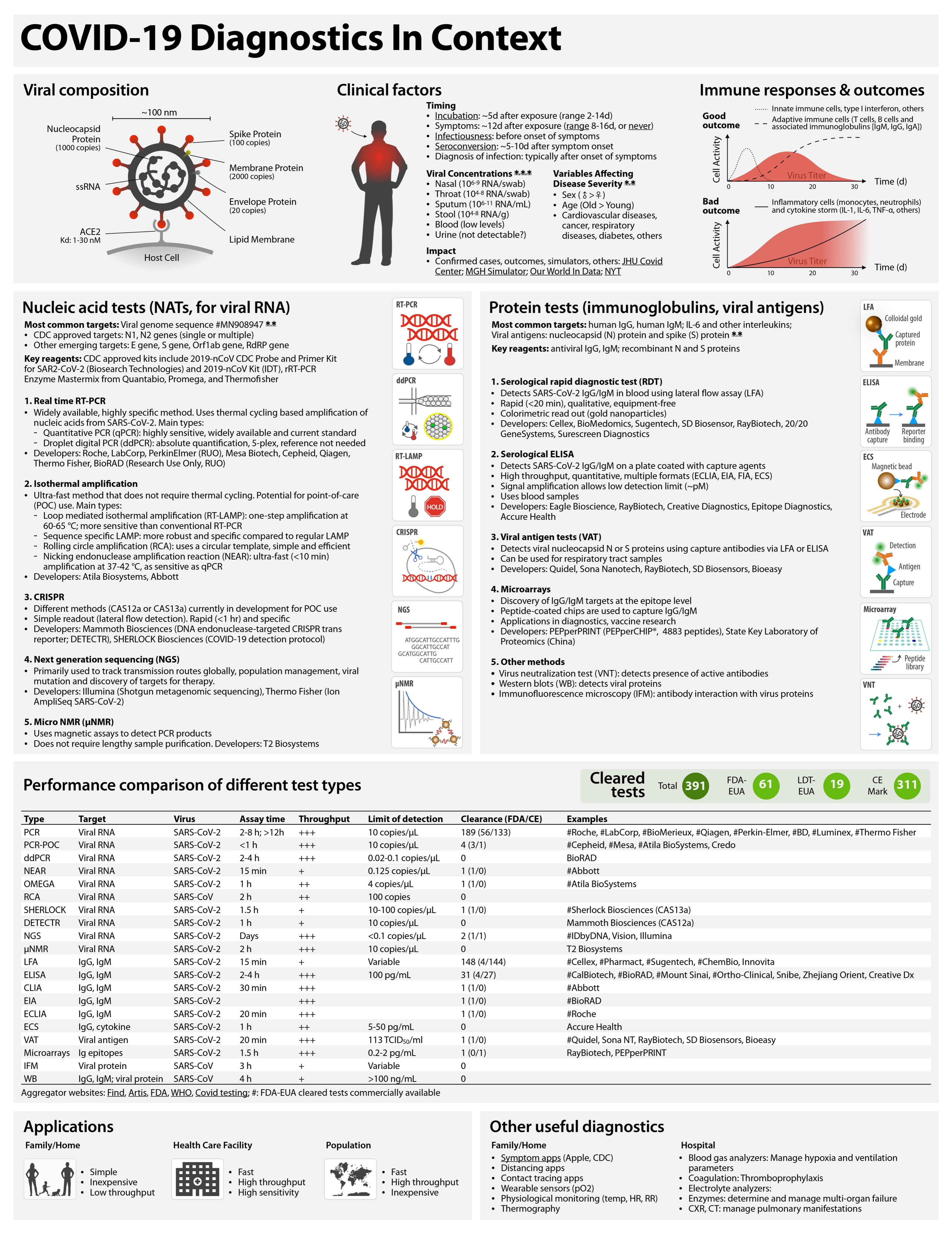
COVID-19 tests can be grouped as nucleic acid, serological, antigen, and ancillary tests, all of which play distinct roles in hospital, point-of-care, or large-scale population testing.
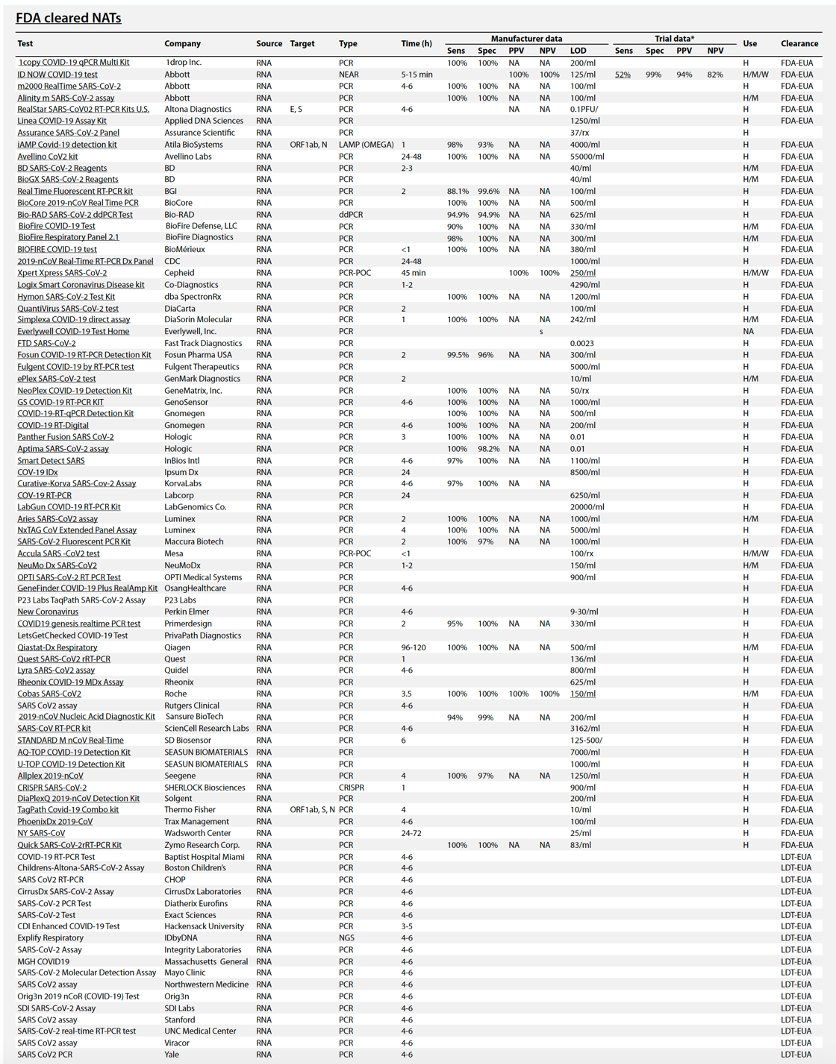
Table 1 summarizes the existing and emerging tests, current at the time of writing (May 2020). A continuously updated version of this table is available at https://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/covid
Eric Topol says:
There are now *88* @US_FDA cleared (by EUA) #COVID19 tests so far. Their false negative rates range from 10-48% (by post-release reports).
Might be better to have less tests, more accuracy, with faster turnaround
I agree.
Table 1 Performance comparison of different test types.
Throughput is determined by process type and assay time. In general, automated plate-based assays have higher daily throughputs. Hashtag (#) indicates example systems that have received FDA emergency use authorization (FDA-EUA). See https://csb.mgh.harvard.edu/covid to access continuously updated information. PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PCR-POC, PCR–point-of-care; ddPCR, digital droplet PCR; NEAR, nicking endonuclease amplification reaction; RCA, rolling circle amplification; SHERLOCK, specific high-sensitivity enzymatic reporter; DETECTR, DNA endonuclease-targeted CRISPR transreporter; NGS, next-generation sequencing; μNMR, micro–nuclear magnetic resonance; LFA, lateral flow assay; ELISA, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; CLIA, chemiluminescence immunoassay; EIA, enzyme immunoassay; ECLIA, electrochemiluminescence immunoassay; ECS, electrochemical sensing; VAT, viral antigen assay; IFM, immunofluorescence microscopy; WB, Western blot.
| Type | Target | Virus | Assay time | Process type | FDA-EUA | Examples |
| PCR | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 2–8 hours; >12 hours | Plate | 56 | #Roche, #LabCorp,
#BioMerieux,
#Qiagen,
#Perkin-Elmer,
#Becton Dickinson,
#Luminex, #Thermo
Fisher, others |
| PCR-POC | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | <1 hour="" td=""> | Cartridge | 2 | #Cepheid, #Mesa,
Credo |
| ddPCR | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 2–4 hours | Manual | 1 | #BioRAD |
| NEAR | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 15 min | Cartridge | 1 | #Abbott |
| OMEGA | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 1 hour | Plate | 1 | #Atila BioSystems |
| RCA | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV | 2 hours | | 0 | |
| SHERLOCK | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 1.5 hours | Kit | 1 | #Sherlock
Biosciences
(CAS13a) |
| DETECTR | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 1 hour | Kit | 0 | Mammoth
Biosciences
(CAS12a) |
| NGS | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | Days | | 1 | #IDbyDNA, Vision,
Illumina |
| μNMR | Viral RNA | SARS-CoV-2 | 2 hours | Cartridge | 0 | T2 Biosystems |
| LFA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | 15 min | Cartridge | 3 | #Cellex,
#Sugentech,
#ChemBio, Innovita |
| ELISA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | 2–4 hours | Plate | 4 | #Mount Sinai,
#Ortho-Clinical (2),
#EUROIMMUN US
Inc., BioRAD, Snibe,
Zhejiang orient,
Creative Dx |
| CLIA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | 30 min | Cartridge | 2 | #Abbott, #DiaSorin |
| EIA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | 2 hours | Plate | 1 | #BioRAD |
| MIA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | | Plate | 1 | #Wadsworth Center |
| ECLIA | IgG, IgM | SARS-CoV-2 | 20 min | Plate | 1 | #Roche |
| ECS | IgG, cytokine | SARS-CoV-2 | 1 hour | Cartridge | 0 | Accure Health |
| VAT | Viral antigen | SARS-CoV-2 | 20 min | Cartridge | 1 | #Quidel, Sona NT,
RayBiotech, SD
Biosensors, Bioeasy |
| Microarrays | Ig epitopes | SARS-CoV-2 | 1.5 hours | Plate | 0 | RayBiotech,
PEPperPRINT |
| IFM | Viral protein | SARS-CoV | 3 hours | Manual | 0 | |
| WB | IgG, IgM; viral protein | SARS-CoV | 4 hours | Manual | 0 |