Supporting Biomarker-Driven Therapies in Oncology: A Genomic Testing Cost Calculator
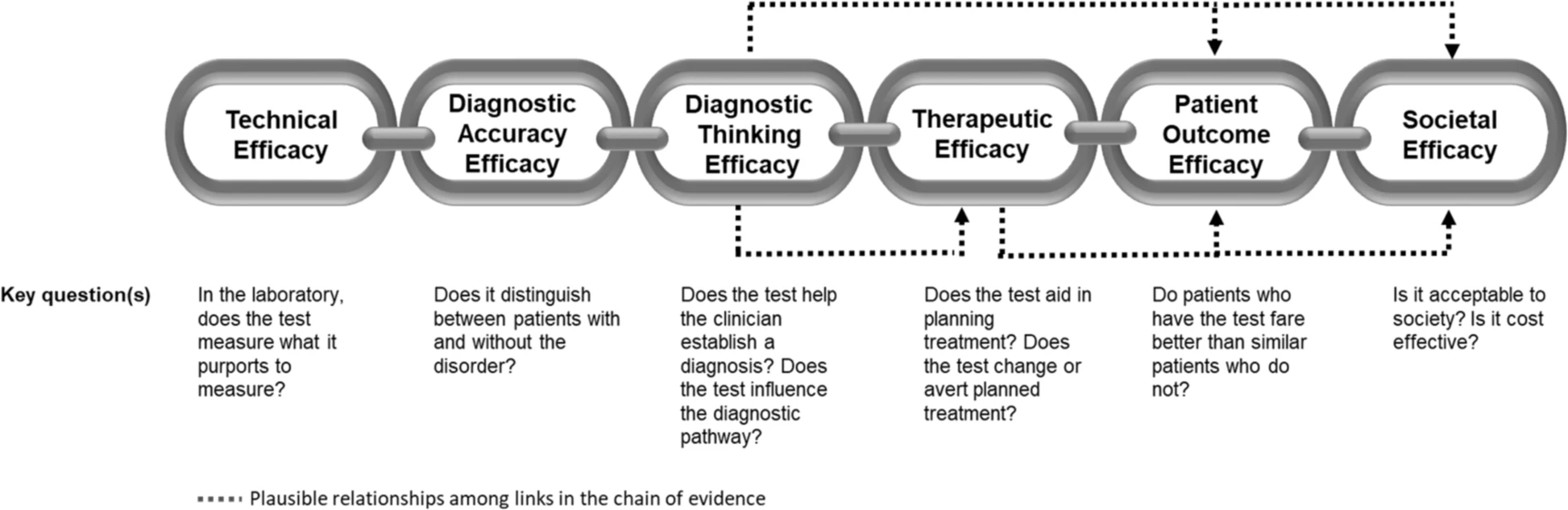
Aquest és un tema amb moltes singularitats i cal estar atents als detalls. Entendre el cost-efectivitat de les proves diagnòstiques obliga a precisar molt què es pretén i com la prova diagnòstica modifica la decisió clínica. És per això que s'hauria d'aplicar el cost per persona identificada correctament com a punt de referència clau. Ara bé això no és senzill de calcular.
Ara tots els ulls estan posats en seqüenciar l'exoma, i un article recent arriba a aquesta conclusió:
On the basis of the available evidence and present findings, exome sequencing as a cost-effective option could have the potential to be used as a genomic test to diagnose suspected genetic disorders. However, there is still no consensus among studies on performing the exome sequencing test as a first- or second-line diagnostic test. While NGS methods are usually implemented as the last diagnostic test by reason of their relatively high cost, a number of recent studies have indicated that when exome sequencing is implemented as a first-line test, extra examinations avoided for diagnosed patients may amply compensate for the cost of the test.
Per tant deixa oberta la qüestió i no respon a la pregunta. Jo crec que és qüestió de dies, seqüenciar l'exoma es convertirà en l'estandard.
PS. Més material.