Foundation models for generalist medical artificial intelligence
La revista Nature publica aquesta setmana un article de revisió que explica l'estat de situació de la Intel·ligència Artificial mèdica generalitzada GMAI. Fa unes setmanes explicava en una entrada els models multimodals, i ara anem més enllà. El concepte generalista ens condueix cap a models que van més enllà de tasques, i que aprenen del context, modelitzen el llenguatge i introdueixen l'aprenentatge contrastat. Per fer-nos una idea, fins ara tot els prop de 500 models d'IA que ha aprovat la FDA eren orientats a 1 o 2 tasques. El salt cap a la IA generalista suposa un canvi substancial. I això ha passat amb pocs mesos de diferència.
Les tres capacitats clau:
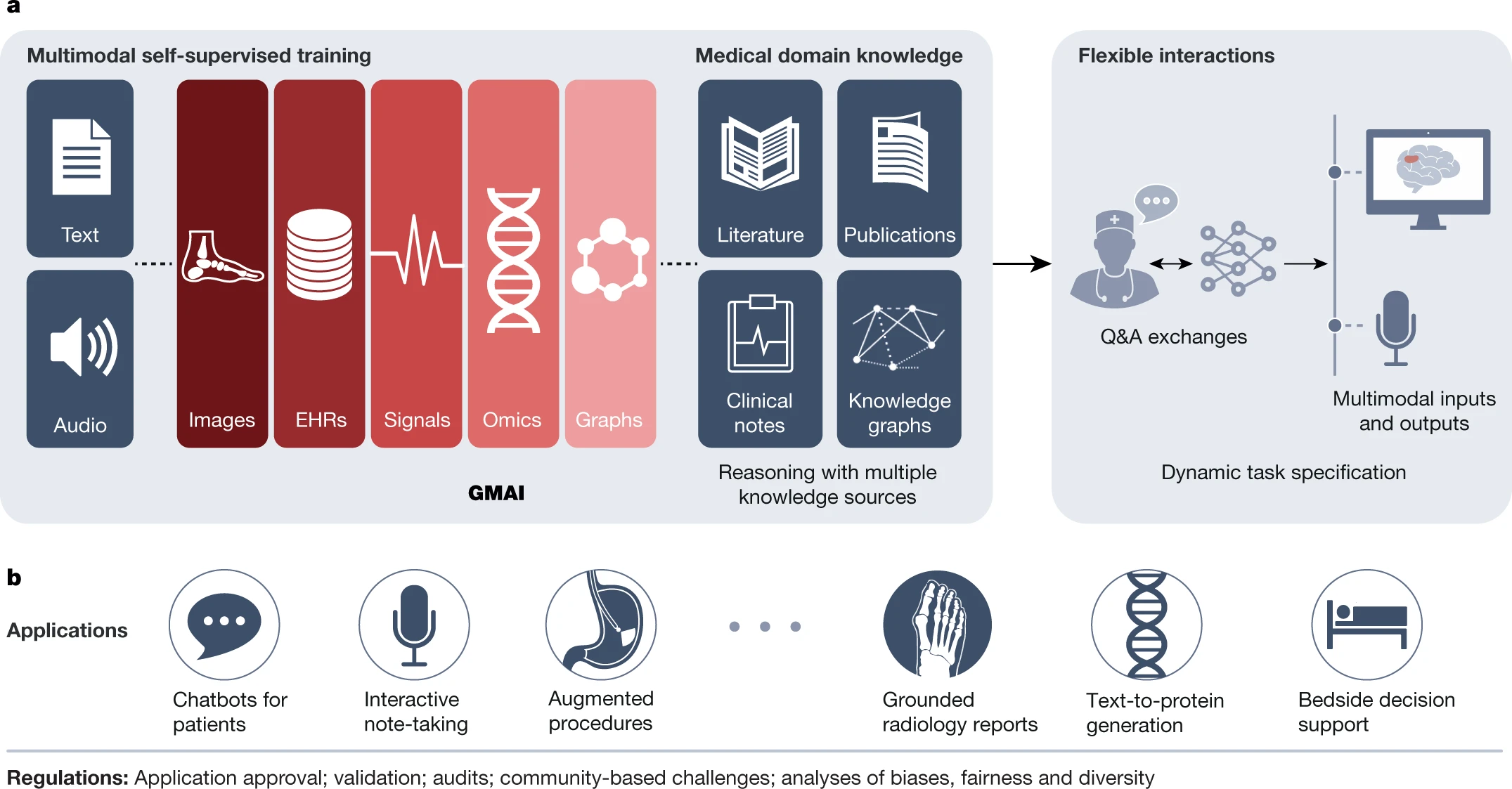
First, adapting a GMAI model to a new task will be as easy as describing the task in plain English (or another language). Models will be able to solve previously unseen problems simply by having new tasks explained to them (dynamic task specification), without needing to be retrained3,5. Second, GMAI models can accept inputs and produce outputs using varying combinations of data modalities (for example, can take in images, text, laboratory results or any combination thereof). This flexible interactivity contrasts with the constraints of more rigid multimodal models, which always use predefined sets of modalities as input and output (for example, must always take in images, text and laboratory results together). Third, GMAI models will formally represent medical knowledge, allowing them to reason through previously unseen tasks and use medically accurate language to explain their outputs.
a, A GMAI model is trained on multiple medical data modalities, through techniques such as self-supervised learning. To enable flexible interactions, data modalities such as images or data from EHRs can be paired with language, either in the form of text or speech data. Next, the GMAI model needs to access various sources of medical knowledge to carry out medical reasoning tasks, unlocking a wealth of capabilities that can be used in downstream applications. The resulting GMAI model then carries out tasks that the user can specify in real time. For this, the GMAI model can retrieve contextual information from sources such as knowledge graphs or databases, leveraging formal medical knowledge to reason about previously unseen tasks. b, The GMAI model builds the foundation for numerous applications across clinical disciplines, each requiring careful validation and regulatory assessment.
Tres aplicacions potencials:
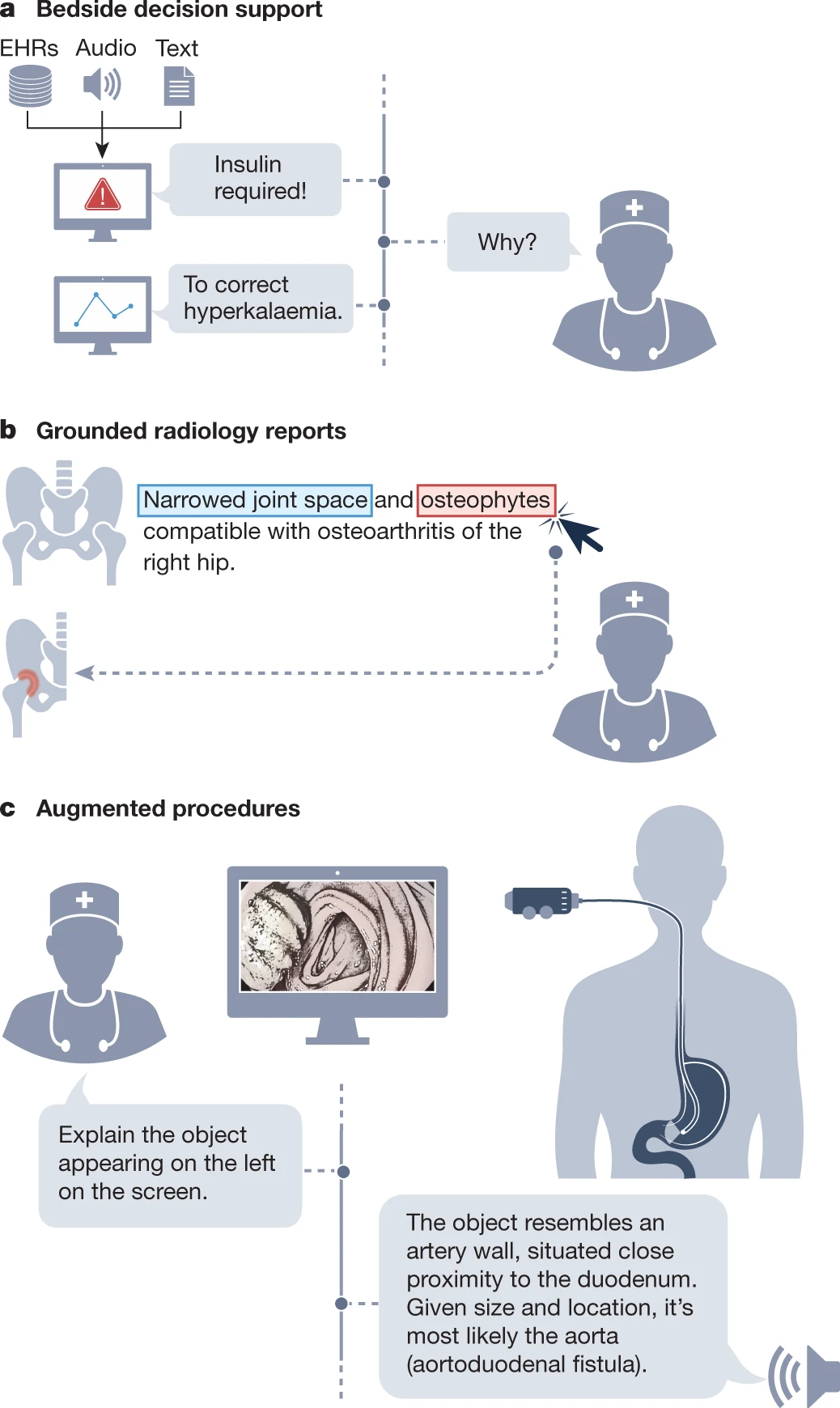
a, GMAI could enable versatile and self-explanatory bedside decision support. b, Grounded radiology reports are equipped with clickable links for visualizing each finding. c, GMAI has the potential to classify phenomena that were never encountered before during model development. In augmented procedures, a rare outlier finding is explained with step-by-step reasoning by leveraging medical domain knowledge and topographic context. The presented example is inspired by a case report58. Image of the fistula in panel c adapted from ref. 58,
L'aplicació de la IA a la medicina representa una impuls transformador crucial, i encara no en sabem les conseqüències. L'article detalla alguns dels reptes, cal llegir-lo per fer-nos una idea de cap on va la cosa.
PS. Per entendre el context de l'article, Eric Topol al seu blog.