A book that explains that shifting financial risk onto doctors in a profit-making system seriously damages patient trust. In addition this undermines overall social capital, which in turn has been linked to health outcomes.
19 d’agost 2021
12 d’agost 2021
04 d’agost 2021
Reordering our society is possible
What We Owe Each Other.A New Social Contract for a Better Society
A thought -provoking book. Chapter 5 is devoted to Health:
Being healthy is the most important determinant of our wellbeing. Physical and mental health (subjective well-being as it is called in the academic research) rank at the top of every major study of happiness across the world. Ultimately, this is why every society aspires to provide health care for its population. And because the costs of providing health care are reduced when a large population pools its resources, and because a healthy labour force is also good for the economy, the social contract in every society includes health care in some form or another.
The great issues:
- Defining a Minimum for Universal Health Care
- How Should Health Care Be Provided?
- Health Spending Is Only Going Up
- A More Digital Future for Health
- Individual and Social Responsibilities – Where Is the Balance?
We owe each other more. A more generous and inclusive social contract would recognise our interdependencies, provide minimum protections to all, share some risks collectively and ask everyone to contribute as much as they can for as long as they can. This is not about increasing the welfare state, but about investing in people and building a new system of risk sharing to increase overall well-being. Change will come inevitably because the forces of technology, demography and environmental pressures will drive it. The question is whether we prepare for that change or continue to allow our societies to be buffeted by these powerful forces, as we have in recent decades. This book lays out the challenges we face and provides a menu of alternatives for a better social contract around families, education, health, work, old age and between the generations. It is not a blueprint, but it provides a direction of travel that is economically feasible. Nor is it a fixed menu – countries may choose to implement some elements and not others depending on their values and preferences.
03 d’agost 2021
Pharma industry regulation: extracting or creating value
The Global Pharmaceutical Industry. The Demise and the Path to Recovery
The pharmaceutical industry has reached a tipping point. Its business growth is predicated upon fagrantly raising drug prices (especially in the U.S.), thereby increasing the inability of patients to afford medications. The clinical trials that provide the basis for pharma’s new drug development rely on biased designs to favor approvable outcomes, even as sponsors selectively publish mainly the reports that contain favorable results for their test drugs. The industry’s research process exerts a corrupting infuence on medical researchers and the channels of medical communication, while its everyday product promotions involve regular payments of financial and other inducements to prescribers that effectively constitute bribes. Even its involvement in continuing medical education poses a confict of interest and a corrupting infuence on medical practitioners.
If pharma continues operating in this manner, it cannot complain when citizens worldwide demand their governments impose onerous restrictions. Each passing week sees the emergence of additional outrages that make such controls more likely.
Any generalization doesn't fit with an objective observation of reality. However, in chapter 5, you'll find proposals for a new regulation.
29 de juliol 2021
28 de juliol 2021
The relationship between value and values
Value(s). Building a Better World for All
This book focuses on four major crises-the Global Financial Crisis, the Global Health Crisis, Climate Change and the 4th Industrial Revolution– and proposes responses to each. Quite a complicated issue. Therefore, my suggestion is to skip the first 2 parts, and go straight to chapter 14. And a key message:
Purpose, values and trust are not natural concepts for economists. The classic economic view, developed by Nobel laureate Ronald Coase, is that a company is a network of contracts in which everyone – owners, managers and workers – responds rationally to incentives. According to Coase’s The Nature of the Firm, the boundaries of the firm are defined by the differences in costs of providing a good or service through the market or a firm.48 Market transactions bear the costs of searching and gathering information, as well as of bargaining, policing and enforcement. Internalising these transactions within firms saves cost but at the expense of span of control, complexity and diseconomies of scale. The boundary of the firm is determined by the balance of these factors, with those activities that can be performed more efficiently and best done by command and control occurring within firms and the rest mediated through markets.
A strict interpretation of this approach misses how shared purpose can reduce transaction costs allowing activities outside the firm to become shared investments that advance the firm’s purpose, reinforcing its profitability and creating shared value. Shared purpose can alter the boundary of the firm (while increasing its ability to create value) by lowering transaction costs in market relationships as well as by making larger and more complex corporate entities possible. Confidence in shared purpose reduces the need for costly, fully complete contracts with suppliers and customers. At the same time, clarity of purpose within organisations, reinforced by strong internal culture, can lead to a type of continuous innovation that turns good companies into great ones.
This is important because, not for the first time, simple theoretical economic models can be poor guides to business in practice. A contractual model is only as good as the contracts, which in practice can be incomplete, difficult to enforce and subject to default. The assumption that human incentives will be solely guided by contractual terms is belied by the realities of people’s behaviours in a wide range of economic circumstances. Moreover, different parties have different time horizons and interests, which frustrate the achievement of optimal outcomes. As Martin Wolf argues, ‘If the rationale for the corporation is to substitute relational contracts, and so trust, for explicit contracts, and so enforcement, one cannot ignore this in deciding what businesses are for and who should control them.’49
The crucial insights of principal–agent theory are not limited to the need to align incentives of shareholders and management but extend to similar challenges between directors, management and employees as well as between companies and their suppliers and communities. When time horizons differ, there will always be incentives for one party to promise one thing and then renege. As we saw in Chapter 4, this is one of the classic motivations for delegated authority to central banks. And even that elegant solution has its limitations, underlining the importance of a shared mission and values.
A strong corporate culture is part of the solution to the problems of incomplete contracts and imperfect incentives. A strong corporate culture encourages stakeholders to internalise the behaviours firms want to create and sustain. In particular, purpose is indispensable to a culture of integrity. As we have seen, trust cannot be achieved merely by asserting rules and following protocols, but rather it is earned by multiple social interactions that reinforce behaviours and values. What are variously termed moral sentiments, social memes or behavioural cascades matter.
Thus purpose operates on a number of planes. First, internally, it creates the necessary social capital within the firm to underwrite foundations of value creation: tightly functioning teams, and high employee participation and engagement. Second, externally, it operates as a means of generating focus on customer service and alignment. The company’s external focus relates to the traditional purpose of a company: to serve its customers.50 If a firm does this well, it generates customer loyalty, and with time the consumer will become a stakeholder, reinforcing trust, good faith and fair dealing. Third, purpose operates as a social narrative, in communities and societies beyond the firm, helping to create and sustain the firm’s social licence to operate. At the highest level, purpose captures the moral contribution of companies to the betterment of the world now and in the future.
A firm is more than a nexus of contracts. However, how do we define it precisely is still unknown.
27 de juliol 2021
26 de juliol 2021
24 de juliol 2021
Digital health transformation
Empowering the health workforce to make the most of the digital revolution
From the OECD report on digital health trasnformation:
To address these issues to successful digital transformation, governments will need to provide the necessary political leadership and implement a range of policy actions to support three main objectives:
1. building trust in the benefits of digital transformation among health workers and patients while minimising any risks;
2. advancing expertise and skills needed for effective use of digital health technologies;
3. adapting the organisation of health service delivery and the related legal and financial
frameworks.
23 de juliol 2021
On Amazon (anything but a river)
Amazon Unbound. Jeff Bezos and the Invention of a Global Empire
Twenty years ago, everybody thought that Amazon was going to sell books. Now that they have entered into health arena, it's the time to read this timely book.
22 de juliol 2021
21 de juliol 2021
Our fragile world
Death, Grief and Loss in the Context of COVID-19
Outline of the book:
Introduction: Capturing the beginning of a long journey of loss, trauma and grief Panagiotis Pentaris
PART 1: Reconsidering Death and Grief in Covid-19
Chapter 1. Familiarity with death
Chapter 2: Grief in the COVID-19 pandemic
Chapter 3: Apocalypse now: COVID-19 and the crisis of meaning
Chapter 4: Physically distant but socially connected: Streaming funerals, memorials and ritual design during COVID-19
Chapter 5: Social death in 2020: Covid-19, which lives matter and which deaths count?
PART 2: Institutional Care and Covid-19
Chapter 6: End-of-life decision-making in the context of a pandemic
Chapter 7: NHS Values, Ritual, Religion, and Covid-19 Death
Chapter 8: Non-COVID-19 related dying and death during the pandemic
Chapter 9: Covid-19 and care home deaths and harms: A case study from the UK
Chapter 10: Impact of Covid-19 on mental health and associated losses
Chapter 11: Assisted dying and Covid-19
PART 3: Impact of COVID-19 in Context
Chapter 12: Losing touch? Older people and COVID-19
Chapter 13: Between cultural necrophilia and African American activism: life and loss in the age of COVID
Chapter 14: The biopolitics and stigma of the HIV and Covid-19 Pandemics
Chapter 15: Suicide in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic
Chapter 16: Death and dying during the COVD-19 pandemic: The Indian context
20 de juliol 2021
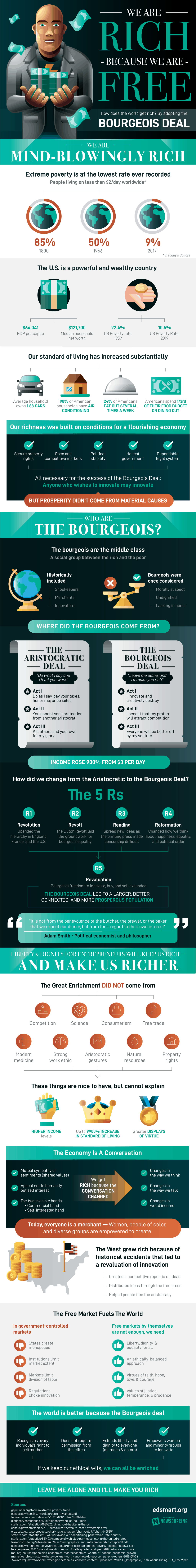
The bourgeois deal
Leave Me Alone and I’ll Make You Rich. HOW THE BOURGEOIS DEAL ENRICHED THE WORLD
by DEIRDRE NANSEN MCCLOSKEY AND ART CARDEN
El llibre "Leave Me Alone and I'll Make You Rich: How the Bourgeois Deal Enriched the World" de Deirdre Nansen McCloskey i Art Carden argumenta que el "Bourgeois Deal" (tracte burgès) ha estat la clau per a l'enriquiment significatiu del món. Aquest tracte, articulat per un home burgès en una cafeteria de Londres el 1820 o per una dona burgesa el 2020, es resumeix en la frase del títol: "Deixa'm en pau i t'enriquiré". Els autors defineixen "burgès" com pertanyent a la classe mitjana urbana, amb mentalitat empresarial.
El llibre ofereix una predicció optimista que el món prosperarà enormement si la gent afavoreix la llibertat i la seva teoria, el liberalisme en el sentit clàssic nascut fa dos segles. McCloskey i Carden sostenen que l'enriquiment massiu del món no es deu principalment a explicacions materialistes, sinó a canvis en l'ètica, la retòrica i la ideologia dels europeus del nord-oest i, ara, del món, que van conduir al liberalisme, l'innovisme i l'enriquiment. Aquest llibre és presentat com una elaboració popular de la trilogia acadèmica anterior de McCloskey sobre l'Era Burgesa.
Els autors il·lustren la magnitud d'aquest enriquiment comparant la vida de Fantine a "Les Misérables" el 1832 amb la d'una mare soltera amb dos fills a Birmingham, Alabama, el 2014. Tot i que la situació a Birmingham no és ideal, és vastament més còmoda materialment que la de Fantine, amb accés a aigua corrent, sanitat que funciona, alfabetització i suficient per menjar. Aquest "frenètic millorament" portat pel Tracte Burgès ha multiplicat les veus en la conversa artística i espiritual, tant com el menjar i el refugi. L'èxit al carrer Beale a Memphis, "la llar del blues", requeria un esperit emprenedor i una ment creativa, possibles gràcies als permisos del Tracte Burgès i a l'abundància moderna d'instruments musicals.
El nucli ètic del Tracte Burgès es descriu com l'orgull de ser un "comerciant just", amb una indústria tranquil·la i tenaç, fent concessions i mostrant consideració, i buscant la millora contínua en els negocis que generen intercanvis mutuament avantatjosos. Aquest tracte ha competit amb altres quatre maneres d'organitzar la societat que substitueixen la cooperació per la coerció: el Tracte de la Sang Blava (aristocràtic), el Tracte Bolxevic, el Tracte Bismarkià (estat del benestar modern) i el Tracte Burocràtic. Els autors argumenten que aquests últims han conduït a la pobresa, la matança o han imposat obstacles als innovadors.
El Tracte Burocràtic, en particular, es caracteritza per la lògica de "Mare, puc innovar?", on el millorament es realitza per permís d'una aristocràcia d'experts, sovint resultant en estancament tecnològic. En contrast, el Tracte Burgès respon a aquests altres amb un "ocupa't dels teus assumptes". Argumenta que l'emprenedor és responsable davant els banquers, els empleats, els proveïdors i, sobretot, els clients que voten amb els seus diners. La regulació burocràtica, tot i que pretén protegir els consumidors, sovint protegeix els interessos tradicionals de la competència, i és menys eficaç que una opinió pública activa en una societat amb llibertat d'expressió.
El llibre també explora la història canviant de la percepció de la burgesia. En contrast amb obres com "The Shoemaker's Holiday" de Thomas Dekker (1599), que sembla "burgesa" però celebra la jerarquia antiburgesa, "The London Merchant" de George Lillo (1731) va inaugurar la "tragèdia burgesa", donant veu i fins i tot honor a la gent de negocis. Aquesta obra reflecteix una nova valoració dels comerciants honestos i de la dignitat de la seva professió. La Revaluació també es manifesta en "Don Quixote" de Cervantes (1605), on el noble Quixot representa qualitats que van portar al fracàs econòmic espanyol, en contrast amb el pragmàtic Sancho Panza.
La difusió de la lectura gràcies a la premsa d'impremta i la Reforma van ser factors crucials per a l'ascens del Tracte Burgès. La traducció de la Bíblia a llengües vernacles va permetre una participació religiosa més àmplia i va fomentar l'individualisme. Adam Smith és presentat com un articulador clau de la ideologia del Tracte Burgès, defensant la importància del coneixement local i la iniciativa individual per sobre de la planificació estatal, sempre dins d'un marc ètic. Smith va elogiar la "integritat absoluta i la senzillesa de maneres" dels comerciants, juntament amb l'amor per l'aprenentatge i la generositat.
En conclusió, "Leave Me Alone and I'll Make You Rich" defensa que el Tracte Burgès, basat en la llibertat econòmica i la dignitat de la innovació i el comerç, ha estat la força motriu darrere de l'enriquiment sense precedents del món. Els autors conviden a la societat a alliberar els adults perquè puguin aventurar-se, amb la protecció bàsica d'un govern modest, com la millor manera de continuar el progrés.
19 de juliol 2021
Economic science needs humanities
Bettering Humanomics. A New, and Old, Approach to Economic Science
The discoveries I have made by responding critically, yet as amiably as I could manage, are two:
1. There seems to be emerging a new and I think more serious and sensible way of doing economic science—quantitatively serious, philosophically serious, historically serious, and ethically serious, too, as I argue in this volume. The economist Bart Wilson and a few others nowadays call it the “humanomics,” as in the title here.4
2. But, I argue in the other volume, neoinstitutionalism, from Douglass North and Daron Acemoglu and many other economists and political scientists, is not the way forward. Scientifically speaking, its factual claims, like those of the other recent neobehaviorist fashions, such as neuroeconomics and behavioral finance and happiness studies, are dubious—or, at best, questionably founded and argued. The neoinstitutionalists, like the others, do not listen, really listen, to the evidence of humans, or to their friends’ scientific questions and objections. Substantively, they treat creative adults like a flock of little children, terrible twos, to whom we need not listen. We need, they say, merely to “observe their behavior,” omitting for some reason linguistic behavior. And then we record the behavior in questionable metrics. The children-citizens will be pushed around with “incentives,” beloved of Samuelsonian economists and econowannabes. From a great height of fatherly expertise in discerning and designing Max U institutions, the neoinstitutionalist looks down with contempt on the merely human actions and interactions of free adults.
A key book by controversial Deirdre McCloskey, this is the outline:
Part I. The Proposal
Chapter 1. Humanomics and Liberty Promise Better Economic Science
Chapter 2. Adam Smith Practiced Humanomics, and So Should We
Chapter 3. Economic History Illustrates the Problems with Nonhumanomics
Chapter 4. An Economic Science Needs the Humanities
Chapter 5. It’s Merely a Matter of Common Sense and Intellectual Free Trade
Chapter 6. After All, Sweet Talk Rules a Free Economy
Chapter 7. Therefore We Should Walk on Both Feet, Like Ludwig Lachmann
Chapter 8. That Is, Economics Needs Theories of Human Minds beyond Behaviorism
Part II. The Killer App
Chapter 9. The Killer App of Humanomics Is the Evidence That the Great Enrichment Came from Ethics and Rhetoric
Chapter 10. The Dignity of Liberalism Did It
Chapter 11. Ideas, Not Incentives, Underlie It
Chapter 12. Even as to Time and Location
Chapter 13. The Word’s the Thing
Part III. The Doubts
Chapter 14. Doubts by Analytic Philosophers about the Killer App Are Not Persuasive
Chapter 15. Nor by Sociologists or Political Philosophers
Chapter 16. Nor Even by Economic Historians
Resum amb IA
El llibre "Bettering Humanomics: A New, and Old, Approach to Economic Science" de Deirdre Nansen McCloskey proposa una nova aproximació a la ciència econòmica anomenada "humanomics". Aquesta perspectiva accepta els models, les matemàtiques, l'estadística i els experiments de l'ortodòxia econòmica actual (circa 2021), però hi afegeix la immensa informació que es pot obtenir sobre l'acció humana en l'economia a partir de les nombroses formes de parla humana. McCloskey argumenta que els economistes haurien de considerar evidència provinent de fonts diverses com les notícies, la retòrica en experiments controlats, el testimoni de gent de negocis, la xafarderia, els experiments interespecífics, la política, les reflexions ètiques i epistemològiques, les històries dels historiadors, les reflexions dels teòlegs, les introspeccions de poetes i filòsofs, les enquestes d'opinió pública i la saviesa de les arts visuals. En resum, la idea central és que els economistes haurien d'utilitzar tota l'evidència disponible per ser científics seriosos.
McCloskey sosté que l'economia, com altres ciències i com la resta de la vida d'una espècie parlant, té una "retòrica", és a dir, utilitza metàfores, històries i epistemologies. L'autora va escriure una trilogia durant els anys 80 i 90 sobre aquest tema, urgint els economistes a ser conscients de la seva retòrica per tal de desenvolupar una ciència madura. Amb aquest nou llibre i el seu acompanyant, "Beyond Behaviorism, Positivism, and Neoinstitutionalism in Economics", McCloskey va més enllà de la forma de la ciència econòmica per centrar-se en l'objecte substantiu: l'economia mateixa té una retòrica.
La proposta de "humanomics" defensa que una ciència econòmica millor ha de tenir en compte la parla i la ment humana més enllà del conductisme. L'autora critica el que anomena "nonhumanomics", que il·lustra amb problemes en la història econòmica. Argumenta que l'economia necessita teories de la ment humana que vagin més enllà del simple conductisme. McCloskey aprèn tant de Faust com de l'arbitratge de la paritat de tipus d'interès cobert, subratllant l'ampli espectre de l'aproximació "humanomics".
Una part crucial de "humanomics" és la importància de la "sweet talk" (conversa amable) en una economia lliure. McCloskey presenta dades empíriques que suggereixen que aproximadament una quarta part de la renda salarial en una societat de gent lliure prové de la persuasió burgesa i femenina, no d'ordres o informació. Posa exemples de diverses professions on una part significativa del temps es dedica a persuadir, des de advocats i jutges fins a directius i professors. Aquesta persuasió és el que fa funcionar el rellotge econòmic. L'economia formal de la màxima utilitat no pot explicar la "sweet talk", tot i que aquesta és de gran importància.
La "killer app" (aplicació estrella) de la "humanomics" és l'evidència que el Gran Enriquiment (l'augment significatiu de la riquesa des de 1800) va sorgir de l'ètica i la retòrica, i no principalment de l'acumulació de capital o l'explotació jeràrquica. McCloskey argumenta que la dignitat del liberalisme, la idea d'honrar socialment totes les persones, juntament amb la llibertat per entrar en nous oficis i protegir la llibertat econòmica, van ser necessàries i suficients per encoratjar la innovació i el creixement. Són les idees, no els incentius per si sols, els que subjacen a aquest enriquiment. El canvi crucial cap al 1700 va ser un clima de persuasió que va portar a la reflexió, l'emprenedoria i el pluralisme del món modern.
McCloskey fa referència a l'obra d'Adam Smith com un practicant primerenc de la "humanomics". El seu primer llibre, "La Teoria dels Sentiments Morals" (1759), tracta sobre com conversem sobre l'ètica, especialment la virtut de la temprança. Fins i tot a "La Riquesa de les Nacions" (1776), Smith menciona la importància de la persuasió en la divisió del treball.
El llibre també aborda dubtes i crítiques a la "killer app" per part de filòsofs analítics, sociòlegs i historiadors econòmics. McCloskey respon a aquestes objeccions, defensant la importància de la "humanomics" i la seva capacitat per explicar el Gran Enriquiment millor que les explicacions materialistes o institucionalistes. Per exemple, critica la visió de Douglass North i els neoinstitucionalistes per negligir el paper autònom de les idees i la retòrica. També respon a les crítiques sobre la manca de definició de "llibertat" o "dignitat humana" i la suposada falta d'atenció a la desigualtat, argumentant que aquests temes es tracten en la trilogia sobre l'Era Burgesa i en altres treballs.
En conclusió, "Bettering Humanomics" proposa una reorientació de la ciència econòmica cap a una perspectiva més humanista que integri la parla, la retòrica, l'ètica i les idees com a factors crucials per comprendre el funcionament de l'economia i, especialment, les causes del Gran Enriquiment. L'autora convida els economistes a escoltar realment la conversa humana per tal de millorar la seva comprensió del món econòmic.