COVID-19. The Greatest Cover-Up in History—From Wuhan to the White House
31 de desembre 2020
30 de desembre 2020
29 de desembre 2020
28 de desembre 2020
27 de desembre 2020
26 de desembre 2020
25 de desembre 2020
24 de desembre 2020
23 de desembre 2020
The profits of opioid addiction epidemic
American Overdose. The Opioid Tragedy in Three Acts
Formerly in this blog you may have read about opioid epidemics. In the US is a great social and public health tragedy. If you want some details about fentanil consumption in Catalonia, check this report (p.153-155).
In the book America overdose, you'll find an exceelent description about what has happened in US in practical terms. Wirtten by a journalist from The guardian, it may help any public health official of any country to understand the huge danger we have to confront. The starting point for McGreal’s deeply reported investigation is the miners promised that opioid painkillers would restore their wrecked bodies, but who became targets of “drug dealers in white coats.” And says (in chapter 21):
It would be a mistake to conclude that responsibility for the opioid epidemic lies only with the greed of the drug companies or that it is shared solely with corrupt doctors and pharmacists who profited from mass prescribing. They were facilitated by politicians, regulators, and a broader medical industry with an agenda or that chose not to see. The opioid makers were helped in that because, for many years, the primary victims were those it was easy to look away from—the “dumbass hillbillies,” as Willis Duncan put it.
Purdue may have targeted some of the poorest parts of Appalachia because that’s where the data said opioids were already being prescribed. But it proved a convenience that these regions were among the most marginalized in the country and the easiest to stigmatize as the drug makers pursued the disreputable tactic of blaming the victims for their addiction.
Like the nineteenth-century opium dealers, the painkiller manufacturers used the power of the huge profits of addiction to keep the faucets of mass prescribing open. The quarter of a billion dollars a year the drug industry spends on lobbying bought the complicity of Congress and organizations such as the American Medical Association through silence and distraction. The din of money drowned out the warnings sounded by Dr. Art Van Zee about the devastation already wrought to his Virginia community in the late 1990s and the research by doctors such as Jane Ballantyne that should have prompted critical questioning of the claims made for opioids. Congress and the FDA were told loudly and clearly that a national disaster was unfolding more than a decade before the CDC’s Tom Frieden called it an epidemic.
Drawing on the tobacco companies’ playbook, opioid manufacturers obscured the evidence of the dangers of their products even when it was staring the industry in the face. Instead, the drug makers and their front organizations sought to discredit those who advocated caution.
22 de desembre 2020
Five levels of care integration
A helpful framework on integrated care from the Health Services Research article:
The framework focuses on how systems are structured and governed, what people who work in the system believe and how they behave, and activities intended to integrate patient care into a single coordinated process within the system. We chose this model because, while there are many different ways to characterize health systems, we wanted to focus on those characteristics that might prove to be meaningful with regard to performance differences.
Hypothetical relationships are depicted in the model using arrows that move from left to right. The five types of integration depicted in the model (structural, functional, normative, interpersonal and process integration) are hypothesized to effect intermediate and ultimate outcomes. From Singer SJ, Kerrissey M, Friedberg M, Phillips R. A Comprehensive Theory of Integration. Med Care Res Rev. 2020;77(2):204, Sage Publications, Inc.
- Structural integration (physical, operational, financial, or legal ties among operating units within a system)
- Functional integration (formal, written policies, and protocols for activities that coordinate and support accountability and decision making among operating units)
- Process (or clinical) integration (actions or activities intended to integrate patient care across people, functions, activities, and operating units within the system). In our discussion, we refer to this as clinical integration.
Structural and functional integration are under the direct control of system executives. Our intent was to understand the kinds of strategic decisions they were making, why they made them, and how they saw their decisions affecting their goals for their systems. Understanding the organizations that make up the systems and the extent to which systems are structurally and functionally integrated is a vital starting point for understanding whether process/clinical integration is happening within systems, how it is happening, or indeed whether it is even possible.
Two additional types of integration—normative and interpersonal.
Normative integration refers to sharing a common culture; interpersonal integration refers to collaboration or teamwork.
21 de desembre 2020
Economics and epidemiology
An Economist's Guide to Epidemiology Models of Infectious Disease
Bossert et al provide some useful information on the structure and use of epidemiology models of disease transmission, with an emphasis on the susceptible/infected/recovered (SIR) model. And they discuss high-profile forecasts of cases and deaths that have been based on these models, what went wrong with the early forecasts, and how they have adapted to the current COVID pandemic.
Understanding the process by which these models’ predictions and insights can be accessed by policymakers has also gained importance. The normal process of writing, vetting, and publishing scientific and economic research is being stretched to its limits given the urgency of the pandemic. Direct and wide dissemination can work for certain types of knowledge: detailed predictions from empirical models lend themselves to the now ubiquitous COVID “dashboards” that make those predictions available to policy-makers and others with just a click or two. There is no reason to believe that the models which have the best designed websites and interfaces are the ones producing the most careful and accurate predictions, though. Conveying more subtle insights, such as how government policies might interact with endogenous social distancing, seems substantially more difficult but no less important. One would hope that robust lines of communication and established respectful relationships between experts and policy-makers could facilitate such dialogues.
20 de desembre 2020
Climate and health
From Health Affairs issue on Climate and Health, first of all:
To accurately describe the health-related costs of climate change, it is important to distinguish between key terms. Climate-sensitive exposures (such as ozone smog air pollution, extreme heat, and extreme precipitation) and health outcomes include those with demonstrated responses to one or more meteorological variables or seasonal patterns.6,7 In recent years, statistical analyses have enabled detection and attribution of the influence of human-caused climate change on extreme weather and other climate-related exposures.8 These climate change–related impacts on the environment include incremental contributions to the frequency and magnitude of extreme rainfall during hurricanes8,9 and increased temperatures during heat waves,10 among others. It is not yet possible to apply analogous methods to directly quantify the attributable portion of climate-sensitive health outcomes to the incremental effects of climate change, as preexisting medical conditions, health vulnerabilities, and multiple exposures are among the many health determinants and causal factors involved. There is currently a knowledge gap that must be addressed for more complete understanding of climate change–related exposure-response relationships.´
Therefore,
Expanded valuation analyses of the costs of climate-sensitive health outcomes are urgently needed to inform public policy. The findings from such studies can be linked to provide a sense of the overall scope of health costs from climate change in communities, cities, states, regions, and countries.
At present, it is difficult to characterize the costs of health harms linked to climate-sensitive exposures in the US. Given the current inability to comprehensively track recent damage, there is limited understanding of the scope of projected future climate-sensitive health risks and costs.
So, there is not any estimate of inaction so far.
19 de desembre 2020
Profiling complex patients
Use of Latent Class Analysis and k-Means Clustering to Identify Complex Patient Profiles
Instead of predictive modeling using costs, this is the right approach from a clinical point of view:
This cohort study analyzed the most medically complex patients within Kaiser Permanente Northern California, a large integrated health care delivery system, based on comorbidity score, prior emergency department admissions, and predicted likelihood of hospitalization, from July 18, 2018, to July 15, 2019. From a starting point of over 5000 clinical variables, we used both clinical judgment and analytic methods to reduce to the 97 most informative covariates. Patients were then grouped using 2 methods (latent class analysis, generalized low-rank models, with k-means clustering). Results were interpreted by a panel of clinical stakeholders to define clinically meaningful patient profiles.
And the figures below reflect these results.
Great article.
Figure 1. Seven Patient Profiles Derived From Latent Class Analysis
Figure 2. Comparison of k-Means Clustering With Latent Class Analysis (LCA)
Table 1. Baseline and 1-Year Follow-up Characteristics of the Overall Population and by Patient Profile
18 de desembre 2020
How plagues end
From the book:
After its dramatic initial appearance, SARS-2 will ultimately become endemic; it will regularly circulate among us at some low, steady level. This is connected to the second kind of end, which we have already considered: herd immunity. Here, the pathogen is still around, but it has a much more difficult time reestablishing itself. This resembles a well-vaccinated population for any infectious disease; there are only occasional, small outbreaks among nonimmune people.
By 2022 or so, we will reach this outcome naturally or via vaccination. Of course, if we do rapidly develop and distribute a safe and effective vaccine, we could reach herd immunity with fewer deaths. Based on the fundamental R0 of SARS-2, as we saw in chapter 2, up to an estimated 60 to 67 percent of the population could be affected (or roughly two hundred million people in the United States). The necessary percentage could be lower, closer to 40 to 50 percent, given that social network structure means that different people spread the virus to different extents (as we also saw in chapter 2); or it could be higher, if the epidemic moves extremely fast and we overshoot the level required for herd immunity. Whatever the exact percentage, as a pathogen spreads, some people will die and others will recover and become immune, so eventually the virus will run out of places to go. This is the ordinary, natural way that, biologically speaking, epidemics end.
This is what we mean when we say that a pathogen is under control. But sometimes, plagues are so devastating that a society never recovers. It’s very important to emphasize that, as bad as COVID-19 is, it’s not remotely as bad as epidemics of bubonic plague, cholera, or smallpox that have killed much larger fractions of the population and that have had much larger and longer-lasting effects. Those types of plagues are even associated with the iconography of the Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse, Pestilence riding side by side with War, Famine, and Death. Those epidemics vindicated the adage that “too few of the living were left to bury the dead.”
N. Christakis says at the begining of the book
The god Apollo, for example, was both a healer and the bringer of disease. During the Trojan War, with his silver bow and quiver of arrows, he rained a plague down on the Greeks to punish them for kidnapping and enslaving Chryseis, the daughter of one of his favored priests.
I found myself thinking again about Apollo and his vengeance as I contemplated our own twenty-first-century barrage more than three thousand years after the events described in The Iliad. It seemed to me that the novel coronavirus was a threat that was both wholly new and deeply ancient. This catastrophe called on us to confront our adversary in a modern way while also relying on wisdom from the past.
Excerpts from the last chapter, How plagues end:
The pathogens evolve to respond to us, but we, at a slower pace, also evolve to respond to them. Infectious diseases have been a part of our evolutionary history for so long that they have left a mark on our genes. For instance, humans have evolved genetic changes that have proven useful in coping with malaria beginning over one hundred thousand years ago, tuberculosis over nine thousand years ago, cholera and bubonic plague over six thousand years ago, and smallpox over three thousand years ago.36
Infectious pathogens (even if nonepidemic) have arguably been a crucial selective pressure throughout the evolution of our species.37 The primary killers of human beings across evolutionary time are other human beings. Humans do not have any natural predators that substantially affect survival.38 Except for our microscopic enemies.
The SARS-2 virus is a lot less lethal to people of reproductive age and can be combated with the lifesaving tools of modern medicine, so the impact on human evolution is surely going to be minimal. But, at least in theory, another way epidemics end is that hosts evolve to be resistant. And in fact, we may already have naturally occurring genetic variation in our species that affects the severity of COVID-19 in different populations, which would lay the groundwork for such evolution. Over generations, this can result in changes to the genetic makeup of the afflicted populations.
This social construction of COVID-19 means that the end of the pandemic can also be socially defined. In other words, plagues can end when everyone believes they are over or when everyone is simply willing to tolerate more risk and live in a new way. If everyone willingly risks infection and resumes a semblance of normal life (or, implausibly, if everyone decides to employ physical distancing forever), then the epidemic can be said to have ended, even if the virus is still circulating. We got a glimpse of this phenomenon as well in the summer of 2020 as different states, tired of the lockdowns, acted as if the epidemic were over, even though, biologically speaking, it was not. It was wholly understandable that everyone was eager to leave the epidemic behind as quickly as possible. But the epidemiological reality did not submit to our desires. The pandemic was still claiming roughly a thousand lives per day, although Americans seemed inured to it. Many people, and not just self-interested politicians, seemed to believe the SARS-2 epidemic could end by fiat.
Last paragraph:
Microbes have shaped our evolutionary trajectory since the origin of our species. Epidemics have done so for many thousands of years. Like the myth of Apollo’s arrows, they have been a part of our story all along. We have outlived them before, using the biological and social tools at our disposal. Life will return to normal. Plagues always end. And, like plagues, hope is an enduring part of the human condition.
A must read. This is my preferred book reference on current pandemic.
Figure 16: The mortality impact of COVID-19 in the United States can be quantitatively compared to that of other modern epidemics.
17 de desembre 2020
Nudging effectiveness
From a review article:
We identified 26 studies, where 13 were of high or moderate quality. The most commonly tested nudges were reminders, planning prompts, small financial incentives, and feedback. Overall, 8 of 9 studies with a high or moderate quality ranking, focused on self-management outcomes, i.e., physical activity, attendance, self-monitoring, and medication adherence, found that nudges had significant positive effects.However, only 1 of 4 studies of high or moderate quality, analyzing disease control outcomes (e.g.,glycemic control), found that nudges had a significant positive effect for one intervention arm.In summary, this review demonstrates that nudges can improve chronic disease self-management, but there is hardly any evidence to date that these interventions lead to improved disease control. Reminders,feedback, and planning prompts appear to improve chronic disease self-management most consistently and are among the least controversial types of nudges.
And the message:
There is hardly any evidence to date that these interventions lead to improved disease control.
So now what?
16 de desembre 2020
Episode based payments (3)
Medicare's Bundled Payment Initiatives for Hospital‐Initiated Episodes: Evidence and Evolution
The Impact of Medicare’s Alternative Payment Models on the Value of Care
Bundled payments have been promoted as an alternative to fee‐for‐service payments that can mitigate the incentives for service volume under the fee‐for‐service model. As Medicare has gained experience with bundled payments, it has widened their scope and increased their duration. However, there have been few reviews of the empirical literature on the impact of Medicare's bundled payment programs on cost, resource use, utilization, and quality.
Main messages:
- Evidence suggests that bundled payment contracting can slow the growth of payer costs relative to fee‐for‐service contracting, although bundled payment models may not reduce absolute costs.
- Bundled payments may be more effective than fee‐for‐service payments in containing costs for certain medical conditions.
- For the most part, Medicare's bundled payment initiatives have not been associated with a worsening of quality in terms of readmissions, emergency department use, and mortality. Some evidence suggests a worsening of other quality measures for certain medical conditions.
- Bundled payment contracting involves trade‐offs: Expanding a bundle's scope and duration may better contain costs, but a more comprehensive bundle may be less attractive to providers, reducing their willingness to accept it as an alternative to fee‐for‐service payment.
15 de desembre 2020
Atul Gawande on this pivotal moment
Atul Gawande on Taming the Coronavirus
Can a vaccine be distributed fairly? What will be the impact of a large number of people not taking it—as they say they won’t? Atul Gawande, a New Yorker staff writer who was recently appointed to President-elect Joe Biden’s covid-19 task force, walks David Remnick through some of the challenges of this pivotal moment
And in FT: "I do think that the fundamental disaster of the United States is tying where you get your healthcare to where you work,"
Agree
Podcast in The New Yorker radio:
14 de desembre 2020
Unwarranted variation in clinical practice
Variation is not bad or unwarranted per se. To some extent, variation should always exist, because patients are unique and different. Care could be called appropriate when decisions reflect such differences, especially differences in informed patient preference [1].
Variation may be unwarranted when it cannot be explained by sensitivity to patient characteristics or well-informed preferences. In this perspective, we propose alternative hypotheses for mechanisms underlying unwarranted variation in healthcare and propose new target points for research to better understand, reduce and improve unwarranted variation in care quality in daily medical practice.
A key element in this new focus in research should be on the complex cohesion of network effects, reflective medicine, patient beliefs and objective criteria for treatment choices.
After all these years and the large amount of research on variations in medical practice, it's time to act.
12 de desembre 2020
The social media industrial complex and the tiranny of trends
From the book:
We’ve constructed an expansive, multifaceted machine that spans the globe and conducts the flow of information, opinions, and behaviors through society. This Hype Machine connects us in a worldwide communication network, exchanging trillions of messages a day, guided by algorithms, designed to inform, persuade, entertain, and manipulate us.
The object of this machine is the human psyche. It was designed to stimulate our neurological impulses, to draw us in and persuade us to change how we shop, vote, and exercise, and even who we love. It analyzes us to give us options for what to read, buy, and believe. It then learns from our choices and iteratively optimizes its offerings. As it operates, it generates a data exhaust that traces each of our preferences, desires, interests, and time-stamped, geolocated activities around the world. It then feeds on its own data exhaust, refining its process, perfecting its analysis, and improving its persuasive leverage. Its motivation is money, which it maximizes by engaging us. The more precise it gets, the more engaging and persuasive it becomes. The more persuasive it becomes, the more revenue it generates and the bigger it grows. This is the story of the Hype Machine—the social media industrial complex: how it was designed, how it works, how it affects us, and how we can adapt to it.
11 de desembre 2020
What is the alternative to Friedman’s capitalism?
Milton Friedman 50 Years Later
Angus Deaton says:
“Milton Friedman was one of the foremost thinkers who challenged the post-war Keynesian consensus. He was immensely successful in arguing the pro-market case, and questioning the ability of government to improve on market outcomes. Today, we need to reopen these questions, using new economic thinking and new evidence; is the market bringing the unalloyed benefits that Friedman thought it would? This book is an important contribution to that reevaluation,”
And this is the capitalism that Martin Wolf expects:
“in which companies would not promote junk science on climate and the environment; it is one in which companies would not kill hundreds of thousands of people, by promoting addiction to opiates; it is one in which companies would not lobby for tax systems that let them park vast proportions of their profits in tax havens; it is one in which the financial sector would not lobby for the inadequate capitalisation that causes huge crises; it is one in which copyright would not be extended and extended and extended; it is one in which companies would not seek to neuter an effective competition policy; it is one in which companies would not lobby hard against efforts to limit the adverse social consequences of precarious work; and so on and so forth.”
10 de desembre 2020
The largest global public-health initiative
The COVID-19 vaccines are here: What comes next?
From McKinsey:
As vaccine availability nears, communities and consumers will want answers to many questions, including:
- Is the vaccine effective and safe?
- Who will get vaccinated first?
- Which vaccine will we receive, especially if multiple vaccines are available?
- Where and when can we get vaccinated?
- Will we have to pay?
- Above all, what do we need to worry about?
Although the scale of the task may seem daunting, countries benefit by starting end-to-end planning immediately. Our 6A framework lays out a structured approach to ensure vaccines are available, administrable, accessible, acceptable, affordable, and accountable while taking into account strategic considerations associated with uncertainty (for example, vaccine clinical and technical profile) and building system capabilities (Exhibit 2). We have developed, in granular detail, the individual activities and considerations behind each component of the framework. Through the collective initial effort of the pharma industry, the scientific community, global health institutions, and governments, most elements of the “available” segment of the 6A journey are being addressed
09 de desembre 2020
Platforms as essential services
Competition in Digital Markets
Imagine you own a company, and you see millions of potential customers for a new product. But there is a problem: all these customers live on the other side of a river and the only way to reach them leads over a privately owned bridge. The owner of that sole bridge either prevents you from passing altogether or charges excessive fees. Long story short, if that is the case, this product line and, potentially, your entire business are doomed.
Digital platforms can behave in that manner because they do not face serious competition. The platforms’ monopoly power mainly stems from network effects—that means the participation of additional users almost exponentially increases the utility of the network and creates enormous market entry barriers for potential competitors. The characteristics of data and algorithms further foreclose the markets.
Google, Amazon, Facebook, Apple, and others behave just like the railroads did 100 years ago. Instead of physical infrastructure, like bridges and tunnels, the digital platforms leverage network effects that shield them from effective competition.
To define the suitable remedies and to open the digital economy for competition, we can learn from the past. In the early twentieth century, the railroads controlled critical infrastructure and excluded competitors from crucial markets. The railroad monopolies rested on enormous investments in physical infrastructure that could not be replicated.
After all these years, a clear message, while the regulator is still on vacation.
08 de desembre 2020
07 de desembre 2020
Access to effective medicines (in oncology)
Addressing Challenges in Access to Oncology Medicines Analytical Report
Challenges in access to oncology medicines: Policies and practices across the OECD and the EU
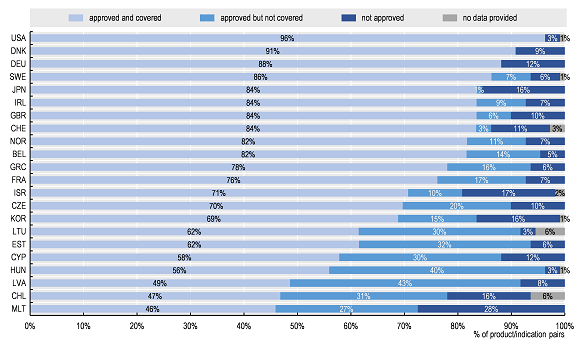
From OECD report:
The data clearly show that access to oncology medicines is unequal across the OECD and EU. Of the 109 product/indication pairs in the sample, the United States had the largest percentage of product/indications approved and covered (by Medicare), followed by Denmark and Germany (96%, 91%, and 88%, respectively). Chile and Malta had the lowest percentage approved and covered (47% and 46% respectively). While access was more homogeneous for a subset of essential medicines (i.e. those included in the WHO 21st Model List of Essential Medicines [WHO-EML]), some of the 31 newer product/indication pairs were not yet approved (or launched) in some countries.
Percentage of total sample of 109 product/indication pairs by approval and coverage status across OECD/EU countries
Note: Data for some countries were not included as many data were missing.Source: Authors based on 2019 OECD survey on challenges in access to oncology medicines.
06 de desembre 2020
Fueling digital health
Healthtech in the fast lane: What is fueling investor excitement?
From McKinsey brief:
As of 2019, digital health represented a global market of approximately $350 billion with many opportunities to compete across multiple subcategories; moreover, the markets for technologies in every value pool are expected to grow by at least 8 percent per annum (Exhibit 2). Understandably, the bulk of digital health players develop technologies that have a direct impact on patient care. About 49 percent of the digital health companies we studied fall into the care-delivery category (that is, offering more effective therapies, providing remote patient support, or supplying therapies to patients)—a $157 billion market (as of 2019) comprising 45 percent of the overall digital health market. Companies in this category either provide novel therapeutic solutions enabled by digital technologies—such as Livongo for diabetes—or use technology to broaden patient access to healthcare solutions, for example, telemedicine company Teladoc (offering remote patient support) or online pharmacy PillPack (supplying therapies to patients). Notably, every value pool in this category is expected to grow by at least 10 percent per annum through 2024.
Digital health’s platform wars are heating up. From Rock health
Few seats available
05 de desembre 2020
Long term care shame
The share of LTC spending in total health spending or as a share of GDP has gradually increased over the last 15 years in many OECD countries as demand for care grows with population ageing and the extension of publicly financed services.
In some countries, spending on LTC has not grown much faster than the economy as a whole. In Slovenia and Spain, for example, the shares of LTC relative to GDP in 2018 were only 0.1-0.2 percentage points above those in 2005, at 1.2% and 0.9% of GDP, respectively.
In Spain, the share of LTC spending has been stagnating since 2009, with LTC spending tracking GDP growth.
04 de desembre 2020
Risks and benefits of self-testing (2)
Direct to Consumer Testing: The Role of Laboratory Medicine
A specific issue on the topic has been released in Clinics in Laboratory Medicine. Inside the issue, you'll find this article: Direct-to-Consumer Tests on the Market Today: Identifying Valuable Tests from Those with Limited Utility 13. This is a key topic. It says:
Debate exists between the consumer and the health care provider when it comes to the value of direct-to-consumer (DTC) testing. At the heart of the issue is the observation that consumers are identifying value in DTC testing as evidenced by an expanding market, and health care providers are skeptical of their value from an analytical and clinical utility perspective. The aim of this article is to briefly review the subject of DTC testing with a specific focus on value from the perspective of the consumer and the health care provider.
Paul Strand at KBr Barcelona
03 de desembre 2020
Trust in professions
In the UK, nurses and doctors are the most trusted professions, with 93 per cent and 91 per cent of the public saying that they trust them to tell the truth. Advertising executives, politicians and journalists receive the lowest scores
02 de desembre 2020
Investing in pandemic preparedness
The Cost Effectiveness of Stockpiling Drugs, Vaccines and Other Health Resources for Pandemic Preparedness
A short review on the topic, many questions, few answers.
Health economics methods can be used to decide the optimal pandemic preparedness strategy based on cost effectiveness because different stockpiling of available measures can be implemented. The economic evaluation of pandemic preparedness strategies and pandemic preparedness measures is based on methods developed for health technology assessment. Nevertheless, this assessment differs from the traditional economic evaluations. The cost-effectiveness evaluation of a new drug compares healthcare costs and health effects for patients treated and not treated with the drug. The cost effectiveness of the drug will depend on the effectiveness of the drug in reducing clinical outcomes and healthcare costs. The drug will be used by the health system in patients with certainty. In contrast to this, the cost-effectiveness evaluation of pandemic preparedness measures and interventions is affected by several facts. First, pandemic preparedness measures are costly because they must be used to prevent and treat pandemic infections in a great number of persons. Second, investments in pandemic preparedness measures could be made many years before the emergence of the pandemic pathogen. Third, the health and economic benefits generated by pandemic preparedness measures will depend on the virulence and infectiousness of the pandemic pathogen. Fourth, pandemic preparedness measures can be associated with large costs and benefits outside the health system and great macroeconomics effects. There is a risk that an unknown pandemic agent will emerge and cause high morbidity and mortality, but we do not know when this will happen or how virulent and infectious a new pandemic agent will be. Although a new pandemic can be similar to previous pandemics, it can be also very different.
Ventilator support and intensive care for acute respiratory failure due to acute respiratory distress syndrome is a cost-effective intervention [8], but the cost effectiveness of stockpiling ventilators depends on the number of stockpiled ventilators and the severity of a future pandemic. The cost effectiveness of ventilator support and intensive care ranges from US$29,000 per QALY in low-risk patients (≥ 70% probability of surviving at least 2 months from the time of ventilator support) to US$110,000 per QALY in high-risk patients (prognostic estimate ≤ 50%) [7]. The question about the optimal number of stockpiling ventilators for pandemic preparedness depends on intervention costs and uncertainty about when the pandemic will happen and how virulent and infectious the pandemic pathogen will be.
Paul Strand at KBr
01 de desembre 2020
Risks and benefits of self-testing
Benefits and Risks of Direct-to-Consumer Testing
These are the pros and cons of two options for the same production process and its impact (a US view only applicable to certain conditions). (Professionalism vs. commercialism).
Conventional:
Self-testing:
And its impact:
Potential and Perceived Benefits of Direct-to-Consumer Testing
Potential Risks of Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) Testing
With DTC testing, consumers may not know the risks or what significance a result has in terms of current and future health. It is challenging for consumers to distinguish tests for health and wellness from entertainment and commercial marketing. This can leave consumers open to misdiagnosis and susceptible to unproven treatments and questionable claims for cancer and disease cures. DTC tests are both an opportunity for an individual to better participate in their health and in the management of chronic diseases, as long as consumers are aware of the risks for inappropriate utilization and inadvertent interpretation that can lead to avoidable follow-up, unnecessary procedures, and additional costs of care. DTC testing is an emerging field and an opportunity for laboratory experts to participate through providing professional advice, consultation on test limitations, interpretive services, and recommendation on optimal test utilization.
My view, now it's time to stop recreational testing and commercialism of lab testing. Later it will be too late.